The Importance of Sleep for Your Mental Health
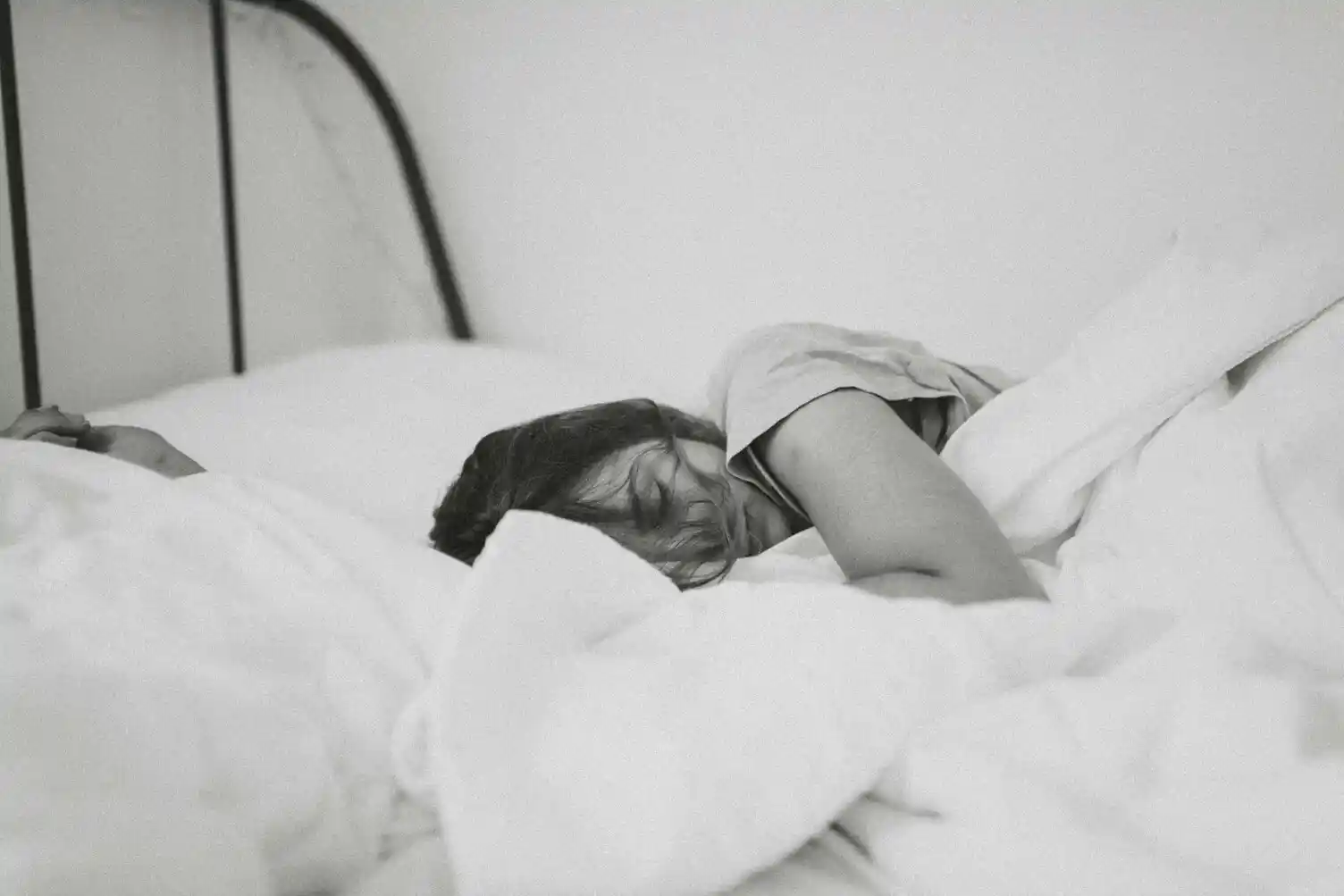
It’s easy to underestimate the role that sleep plays in our mental well-being. After all, sleep is just something we do to rest our bodies, right? Wrong. Sleep is incredibly important for your mental health, affecting everything from your mood to your cognitive abilities. In fact, inadequate sleep can be a major contributor to mental health issues like anxiety and depression.
This article will delve into the science behind sleep and its crucial connection to mental health, as well as tips for improving sleep habits to enhance your overall well-being.
Understanding the Relationship Between Sleep and Mental Health
Why Sleep is Crucial for Your Brain’s Functionality
Sleep is not a passive state where your brain “shuts down.” Instead, it’s a period of intense restoration and repair. During sleep, your brain works to process emotions, form memories, and remove toxins that build up during waking hours. Essentially, sleep is like a brain cleaning service that ensures you function at your best the next day.
The Impact of Poor Sleep on Your Mental State
When you don’t get enough sleep, it affects the brain’s ability to function properly. This can lead to difficulty concentrating, poor decision-making, irritability, and a general inability to cope with stress. Over time, poor sleep can result in heightened feelings of anxiety, depression, and stress. It can even exacerbate existing mental health issues.
The Benefits of Sleep for Mental Health
1. Improved Mood and Emotional Regulation
A good night’s sleep does wonders for your emotional balance. When you sleep well, your brain has the chance to regulate your emotions and restore neurotransmitter balance, making it easier to stay positive and calm.
How Sleep Affects Your Emotions and Stress Levels
Sleep helps your brain process emotional experiences, allowing you to regulate your mood more effectively. Lack of sleep, on the other hand, has been linked to increased emotional reactivity, meaning you may feel more irritable or anxious. This is why a bad night’s sleep can sometimes feel like a snowball effect—one negative emotion after another.
2. Enhanced Cognitive Function and Memory
When you sleep, your brain consolidates memories and strengthens learning pathways, making it easier to retain new information. This means that adequate sleep is essential for both short-term memory and long-term learning.
The Role of Sleep in Brain Function and Learning
Good sleep is crucial for problem-solving and critical thinking as well. Have you ever woken up with a clearer perspective on an issue that seemed complicated the night before? That’s your brain working hard during sleep to organize thoughts and find solutions.
3. Better Stress Management
Sleep is like your body’s natural stress reliever. When you don’t get enough rest, your body produces higher levels of cortisol, the stress hormone. High cortisol levels are associated with increased anxiety and difficulty managing stress. A proper amount of sleep keeps cortisol in check and helps your body respond to stress more effectively.
How Sleep Helps Your Body and Mind Cope with Stress
A good night’s sleep allows the body to recover from stress and recharge, helping you feel more resilient and better equipped to handle the challenges of the day ahead. Without this rest, stress can accumulate, making it harder for your brain to process and regulate emotions.
4. Decreased Risk of Mental Health Disorders
Sleep deprivation has been shown to contribute to the development and exacerbation of mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, and even bipolar disorder. People with chronic sleep problems are also more likely to experience mood swings and cognitive difficulties.
The Connection Between Sleep Deprivation and Anxiety, Depression, and Other Disorders
When you don’t sleep enough, the brain’s emotional regulation systems become compromised, making it harder to handle negative emotions. Over time, this can lead to more serious mental health issues, such as chronic anxiety and depression.
How Sleep Affects Your Brain’s Neurochemicals
Sleep and Neurotransmitters: The Chemical Balance That Impacts Your Mood
Sleep directly influences the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, all of which play a role in mood regulation. Proper sleep helps maintain this chemical balance, leading to a better sense of well-being.
How Sleep Regulates the Stress Hormone Cortisol
Cortisol, often referred to as the “stress hormone,” is regulated during sleep. When you don’t get enough rest, cortisol levels remain elevated, contributing to feelings of stress, anxiety, and even physical health issues such as high blood pressure.
Common Sleep Disorders and Their Impact on Mental Health
Insomnia and Anxiety: A Vicious Cycle
Insomnia, a condition characterized by difficulty falling or staying asleep, is often both a cause and a symptom of anxiety. Poor sleep can trigger anxiety symptoms, while anxiety makes it harder to sleep, creating a harmful cycle.
Sleep Apnea and Its Link to Depression
Sleep apnea, a condition where breathing is interrupted during sleep, has been closely linked to depression. The frequent disruptions in sleep prevent individuals from reaching the deeper stages of restorative sleep, leading to persistent feelings of sadness, irritability, and fatigue.
How Much Sleep Do You Really Need for Optimal Mental Health?
Recommended Sleep Duration Based on Age and Lifestyle
The ideal amount of sleep varies depending on your age and lifestyle. Adults should aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night, while teenagers need 8-10 hours. Understanding your sleep needs and sticking to a schedule is key to improving your mental health.
The Ideal Sleep Quality vs. Quantity for Mental Health
It’s not just about the quantity of sleep, but the quality too. Restorative sleep allows for deep stages of rest where the brain and body rejuvenate. A disturbed or restless night’s sleep can undermine the mental health benefits of sleep, even if you get a full 8 hours.
Tips for Improving Sleep to Boost Your Mental Health
1. Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate your body’s internal clock. This consistency leads to better sleep quality and can improve your mood and energy levels.
Why Regular Sleep Routines Improve Mental Health
Having a set routine signals to your brain that it’s time to wind down, which can help reduce stress and anxiety. Over time, your body will learn to expect rest, making it easier to fall asleep naturally.
2. Create a Restful Sleep Environment
Your sleep environment plays a huge role in your mental health. A cool, dark, and quiet room promotes better sleep. Removing distractions like electronics can make a significant difference in your sleep quality.
How Your Sleep Environment Affects Your Mental and Physical Health
Consider investing in a comfortable mattress and pillows that support restful sleep. A clean, organized environment also contributes to a sense of calm, making it easier to relax before bed.
3. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques like deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and even yoga can help ease tension before bed, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep.
How Meditation, Deep Breathing, and Relaxation Can Improve Sleep
Meditating for just 10-15 minutes before bed can help calm the mind, lower cortisol levels, and prepare your body for rest. These techniques are simple but effective ways to reduce the mental chatter that often keeps us awake.
4. Limit Stimulants and Blue Light Exposure
Avoid caffeine, nicotine, and electronics before bed. Blue light from screens interferes with the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep, making it harder to fall asleep naturally.
How Avoiding Caffeine and Electronics Enhances Sleep Quality
Try limiting screen time at least an hour before bed and opt for relaxing activities like reading or taking a warm bath instead. This will help signal to your body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for rest.
The Link Between Sleep Hygiene and Long-Term Mental Health
Creating Healthy Habits for Sleep and Mental Well-being
Improving your sleep habits and establishing a bedtime routine that supports restful sleep is crucial for long-term mental health. Sleep hygiene involves practices like setting a consistent bedtime, keeping your bedroom cool and dark, and avoiding stimulating activities close to bedtime.
Conclusion
Sleep is essential for your mental health, and the benefits go far beyond feeling rested. It impacts your mood, cognitive function, stress levels, and even your risk of developing mental health disorders. By understanding the importance of sleep and adopting healthy sleep habits, you can improve your mental well-being and overall quality of life.
FAQs
- How does sleep deprivation affect mental health?
Sleep deprivation can lead to increased stress, anxiety, depression, and emotional instability. It also impairs cognitive function, making it harder to manage emotions and stress. - How much sleep do I need for optimal mental health?
Most adults need 7-9 hours of sleep per night, while teenagers require 8-10 hours. Quality sleep is just as important as the quantity, so aim for restorative rest. - Can better sleep improve my mood?
Yes! Getting enough sleep helps regulate emotions, reducing irritability and increasing emotional resilience. - What’s the best sleep environment for mental health?
A cool, dark, and quiet environment promotes better sleep. Invest in a comfortable mattress and remove distractions like electronics for a more restful night. - Can mindfulness techniques really improve sleep?
Absolutely! Mindfulness practices like deep breathing and meditation help calm the mind, reduce stress, and prepare your body for restful sleep.